Self-Hosting Stories
Self-host your StorifyMe stories on your own infrastructure for complete control over delivery, compliance requirements, or custom domain needs.
Prerequisites
- StorifyMe account with API access
- Server infrastructure (AWS S3, Google Cloud Storage, or similar)
- HTTPS-enabled endpoint for webhook
- SSL certificate for your hosting domain
Webhook Setup
Configure webhooks to automatically receive exported stories from StorifyMe.
Configuration
Navigate to Settings → API Settings → Webhooks in your StorifyMe dashboard.
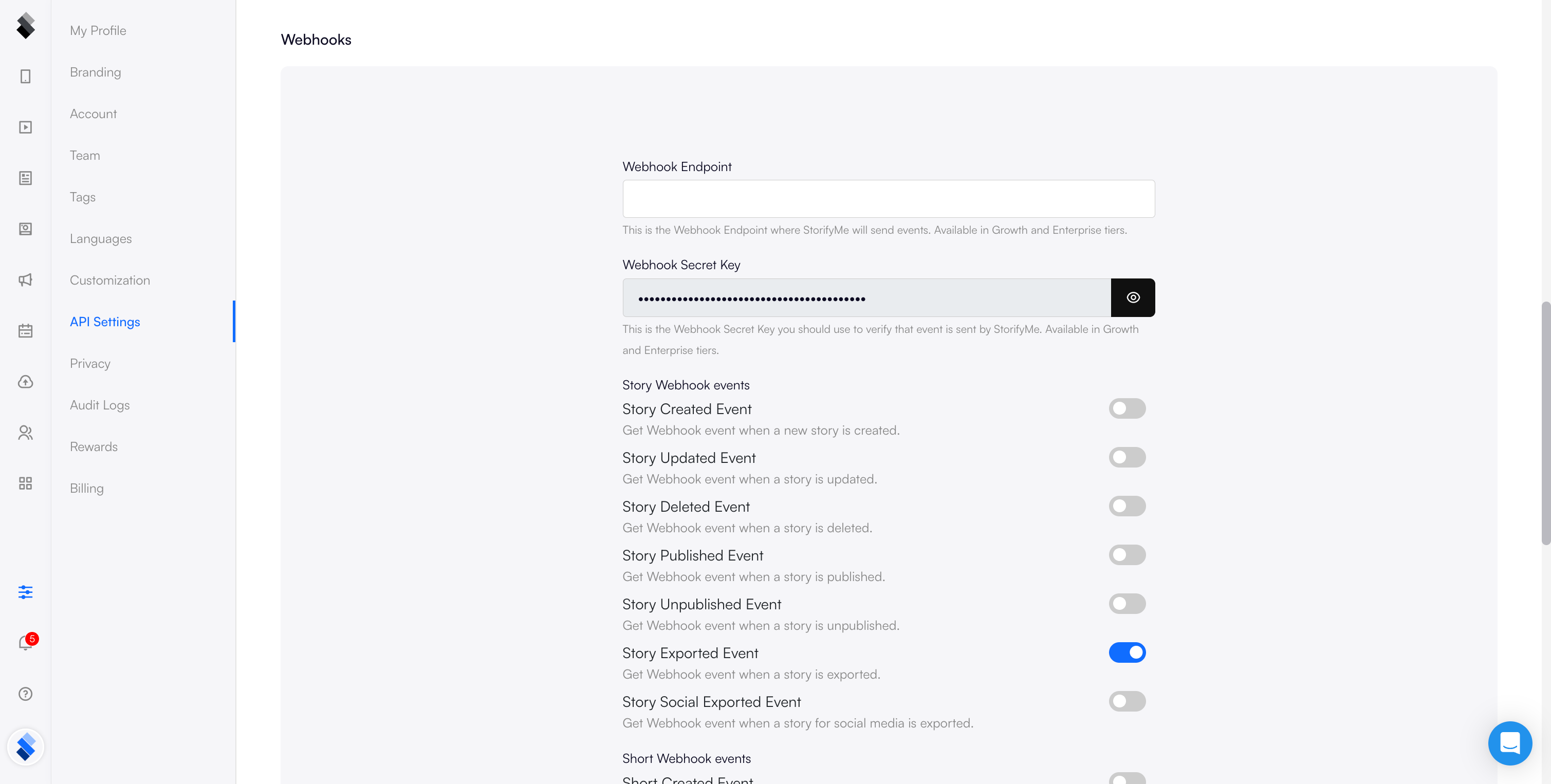
Configure the following:
- Webhook URL: Your server endpoint (e.g.,
https://api.yourdomain.com/storifyme-webhook) - Webhook Secret Key: Used to verify request authenticity
- Events: Select "Story Exported"
Webhook Payload
When a story is exported, you'll receive a POST request with this payload:
{
"id": "st-ev-1",
"type": "story.exported",
"created": 1617024965948,
"data": {
"id": 1,
"file": "story_export_file.zip",
"downloadLink": "https://storifyme.com/api/exports/export/story/download?name=story_export_file.zip&token=one_time_auth_token"
}
}
Webhook Verification
Every webhook request includes X-StorifyMe-Webhook-Signature header for security verification.
Always verify the webhook signature to ensure requests are coming from StorifyMe servers. Never skip this security check in production.
Verify the signature by calculating the hash of the payload:
- Node.js
- Python
const crypto = require('crypto');
function verifyWebhook(payload, signature, secret) {
const hash = crypto
.createHmac('sha256', secret)
.update(Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(payload.data), 'utf-8'))
.digest('hex');
return hash === signature;
}
// Usage in your webhook handler
app.post('/storifyme-webhook', (req, res) => {
const signature = req.headers['x-storifyme-webhook-signature'];
const secret = process.env.STORIFYME_WEBHOOK_SECRET;
if (!verifyWebhook(req.body, signature, secret)) {
return res.status(401).send('Invalid signature');
}
// Process the webhook
if (req.body.type === 'story.exported') {
handleStoryExport(req.body.data);
}
res.status(200).send('OK');
});
import hmac
import hashlib
import json
def verify_webhook(payload, signature, secret):
message = json.dumps(payload['data']).encode('utf-8')
hash_value = hmac.new(
secret.encode('utf-8'),
message,
hashlib.sha256
).hexdigest()
return hash_value == signature
# Usage in your webhook handler (Flask example)
@app.route('/storifyme-webhook', methods=['POST'])
def webhook():
signature = request.headers.get('X-StorifyMe-Webhook-Signature')
secret = os.environ.get('STORIFYME_WEBHOOK_SECRET')
if not verify_webhook(request.json, signature, secret):
return 'Invalid signature', 401
if request.json['type'] == 'story.exported':
handle_story_export(request.json['data'])
return 'OK', 200
Complete Webhook Handler Example
AWS Lambda function that downloads the export and uploads to S3:
const AWS = require('aws-sdk');
const axios = require('axios');
const unzipper = require('unzipper');
const crypto = require('crypto');
const s3 = new AWS.S3();
const BUCKET_NAME = process.env.S3_BUCKET;
const WEBHOOK_SECRET = process.env.STORIFYME_WEBHOOK_SECRET;
exports.handler = async (event) => {
const signature = event.headers['x-storifyme-webhook-signature'];
const body = JSON.parse(event.body);
// Verify signature
const hash = crypto
.createHmac('sha256', WEBHOOK_SECRET)
.update(Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(body.data), 'utf-8'))
.digest('hex');
if (hash !== signature) {
return { statusCode: 401, body: 'Invalid signature' };
}
if (body.type !== 'story.exported') {
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'Event ignored' };
}
try {
// Download the ZIP file
const response = await axios.get(body.data.downloadLink, {
responseType: 'stream'
});
// Extract and upload to S3
const storyId = body.data.id;
const directory = await response.data.pipe(unzipper.Parse());
for await (const entry of directory) {
const fileName = entry.path;
const fileContent = await entry.buffer();
// Upload each file to S3
await s3.putObject({
Bucket: BUCKET_NAME,
Key: `stories/${storyId}/${fileName}`,
Body: fileContent,
ContentType: getContentType(fileName),
ACL: 'public-read'
}).promise();
}
return { statusCode: 200, body: 'Story deployed successfully' };
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error processing story export:', error);
return { statusCode: 500, body: 'Failed to process export' };
}
};
function getContentType(filename) {
if (filename.endsWith('.html')) return 'text/html';
if (filename.endsWith('.js')) return 'application/javascript';
if (filename.endsWith('.css')) return 'text/css';
if (filename.endsWith('.json')) return 'application/json';
if (filename.endsWith('.png')) return 'image/png';
if (filename.endsWith('.jpg') || filename.endsWith('.jpeg')) return 'image/jpeg';
return 'application/octet-stream';
}
Deployment
Upload extracted story files to your hosting solution. Popular options:
- AWS S3 with CloudFront CDN
- Google Cloud Storage with Cloud CDN
- Azure Blob Storage with Azure CDN
- Cloudflare R2
CORS Configuration
Stories won't load without proper CORS headers configured on your hosting.
Your hosting must include these CORS headers:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, HEAD
Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Content-Type
AWS S3 CORS example:
[
{
"AllowedHeaders": ["*"],
"AllowedMethods": ["GET", "HEAD"],
"AllowedOrigins": ["*"],
"ExposeHeaders": []
}
]
CDN Recommendations
Using a CDN improves performance and reduces bandwidth costs:
- Configure caching headers (e.g.,
Cache-Control: public, max-age=31536000) - Enable gzip/brotli compression
- Set up SSL certificate for custom domain
- Configure cache invalidation for story updates
Testing
- Test webhook endpoint with RequestBin or similar tool to inspect payloads
-
Export a test story from StorifyMe dashboard to trigger the webhook
-
Verify deployment by accessing the story URL in your browser (e.g.,
https://cdn.yourdomain.com/stories/123/index.html) -
Test in your app by pointing the SDK to your self-hosted story URL